Medical Device Industry Facts
Medical technology companies create life changing innovation. These advanced medical devices and diagnostics allow people to live longer, healthier and more productive lives.
The medical technology industry—often referred to as medtech—comprises the companies that develop, manufacture, and distribute the technologies, devices, equipment, diagnostic tests, and health information systems that are transforming health care through earlier disease detection, less-invasive procedures, and more effective treatments.
Life-changing medical technologies allow millions of people to live longer, healthier, and more productive lives. The research and innovation to develop these cutting-edge technologies allows the U.S. to continue leading the world in medical advancements. From prosthetics to radiation therapies, medtech changes healthcare for the benefit of patients and health care providers. Our technologies improve quality of life, reduce time spent in hospitals and help loved ones beat life-threatening diseases.
What is a Medical Device?
A medical device is an instrument, apparatus, implant, machine, tool, in vitro reagent, or similar article that is to diagnose, prevent, mitigate, treat, or cure disease or other conditions, and, unlike a pharmaceutical or biologic, achieves its purpose by physical, structural, or mechanical action but not through chemical or metabolic action within or on the body.
Medtech Spurs U.S. Innovation

The U.S. is the largest medical device market in the world, comprising over 40% of the global medtech market.

U.S. exports of medtech have consistently outpaced imports, including a trade surplus of over $1.1 billion in 2017.

Advanced medical devices and diagnostics allow people to live longer, healthier, more productive, and independent lives. From 1980-2019, 5 years were added to the U.S. life expectancy thanks to advancements in medical technology.
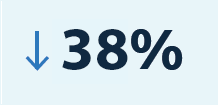
Since 1980, there has been a 38% decrease in the number of patient-days spent in hospitals thanks to medical technologies.
Our Industry
Medical technology innovators are committed to providing physicians and other health care providers with the best tools to diagnose and treat patients. This commitment drives over 6,500 medtech companies in the U.S., which are mostly small- and medium-sized enterprises, to create medical miracles every day.
Industry Facts
These companies, most with fewer than 100 employees, are in the highly competitive business of creating constant progress through constant innovation.
- Our innovations help patients worldwide live longer, healthier and more productive lives.
- We improve the efficiency of health care systems through earlier disease detection and more effective treatments that reduce the economic burden of disease and the cost of care.
- We drive economic growth by creating high-paying manufacturing jobs in the U.S. and through net exports to other countries around the world.
- The market for our products is highly competitive, which helps keep our prices low.
Medical technology saves lives, improves patient outcomes and helps lower the overall cost of health care. It is also one of America’s strongest and fastest-growing manufacturing sectors, creating and producing medical innovations for use around the world—and providing good-paying jobs across the country.

Job Creation
Creating Good-Paying Jobs
The medtech industry directly accounts for nearly 519,000 U.S. jobs.
Safety & Quality
Commitment to Safety, Effectiveness, and Quality
Patient safety is the medical device industry’s #1 priority.

America’s Medical Technology Industry
America’s medical technology companies play a pivotal role in diagnosing and providing quality treatment options for patients, improving outcomes, lowering health care costs and promoting economic growth. Our products range from those developed and used by world leaders in medical science and care—such as nanotechnology, state of the art imaging and genetic testing—to the ones parents use everyday, such as bandages, thermometers and catheters.
The medical technology industry is a manufacturing success story, one of the last expanding manufacturing enterprises in the U.S. that merges rapid innovation with precision product building and distribution. Our industry is a world-leader, with home grown R&D, domestic manufacturing in communities large and small and worldwide exports of American made products. Our economic contributions go beyond conventional measurements of employment, wages and exports—they extend to the increased productivity of the American workforce through greater advances in health.
Innovation is at our core. The advances in medical technology within our own lifetimes is only the beginning of ongoing improvements. America’s core policy and regulatory choices establish the context for future improvements. A strong FDA, appropriate Medicare reimbursement and other policies must be in place to ensure a strong future for patient and health care provider access to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, life-enhancing therapies and continued innovation for the next breakthrough treatments. Medical technology changes lives. We are an engine for growth and a vehicle for personal and health progress.
Disease Areas
The medical technology industry is continually advancing and developing new innovations that improve the health and well-being of patients worldwide.
Antibiotic Resistance
Today, antibiotic resistance is a leading global health problem with a substantial impact on patients, health care systems and economies worldwide. Current trends project antibiotic resistance could cause up to 10 million deaths annually by 2050. Diagnostic tests have the capacity to reduce inappropriate antibiotic use by identifying non-bacterial infections, expedite diagnosis and treatment decisions through point-of-care tests, and guide antimicrobial treatment selection through antibiotic susceptibility tests.
Cancer
This year, more than 1.7 million Americans are expected to receive a cancer diagnosis, and more than 15 million people are currently living with cancer. The medical technology industry is continually advancing and developing new innovations that improve the health and well-being of patients worldwide, including those living with a cancer diagnosis. In fact, the medtech industry invests roughly $2 billion annually into the products and technologies used to diagnose and treat cancer patients throughout every stage of cancer care.
Cataracts
Cataracts are a leading cause of visual impairment among aging Americans and a key quality of life issue. Cataract surgery, the only known treatment, involves removal of the clouded lens and replacement with an intraocular lens (IOL), an artificial lens that requires no care and becomes a permanent part of the eye. Cataract surgery has been shown to help patients in terms of quality of life, better vision, and reduced mortality.
Pain
Pain affects more Americans than diabetes, heart disease, and cancer combined. It is cited as the most common reason Americans access the health care system, and is a major contributor to health care costs. The opioid crisis is killing thousands of Americans each year. As a result, the government has declared the opioid crisis a public health emergency. Today, there are innovative medical technology solutions available that can help play a role in combatting this national crisis. Solutions that have the potential to reduce our country’s dependence on opioids include implants and other devices, as well as apps and diagnostic tests that facilitate effective pain management and help curb the misuse, abuse, and overdose of opioids. Medical technology companies are developing innovations that are minimally invasive, enabling patients to return to routine activities in a shorter period of time while experiencing less pain and discomfort after surgery.
Diabetes
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that one in three U.S. adults could have diabetes by 2050, if recent trends continue at the same rate. Continuous glucose monitoring technology allows patients with Type 1 diabetes to check their glucose levels on a continuous basis, as opposed to three to four times per day, and without a blood draw. For patients who inject insulin, advancements in needle technology—including shorter needles with finer gauge—have been shown to improve the patient experience through reduced pain, and greater ease and convenience. Insulin pumps can provide patients with the insulin they need to stabilize their glucose levels, either on a continuous basis or as needed, such as around mealtime.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women. Every year roughly 735,000 Americans have a heart attack. While lifestyle changes are often the first solution to managing heart disease, medical technology can play an important role in the treatment of advanced cases. Implantable medical devices like pacemakers and implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) help to control heart rhythm, while left ventricular assist devices or LVADs are used to support the heart and circulation.
HIV/AIDS
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 1.2 million people in the United States are living with HIV. Diagnostic tests have various uses and benefits for patients with HIV or AIDS, including determining the presence of the disease and measuring the effectiveness of treatments. Several types of diagnostic tests exist for the detection of HIV/AIDS, including those that test for antibodies or analyze RNA. Another type of diagnostic, CD4 testing, counts T-cells and is used to monitor the immune system function in HIV-positive patients.
Infectious Disease
Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi, and each year millions of Americans are affected by them. Diagnostic tests play a valuable role in the detection and prevention of infectious diseases. Microbiological tests are used to detect disease-causing agents to determine whether a patient has ailments ranging from strep throat to the West Nile virus. Various diagnostic tests have been developed to identify emerging infections and thus help prepare for, prevent, and respond to infectious disease outbreaks.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a leading cause of disability in the U.S., with 27 million Americans suffering from it. Patients with walking impairments from OA are reported to run a risk of early death that is 1.48 times higher than the general population. In fact, 40% of men and 57% of women with knee OA are physically inactive. The CDC reports that 47% of adults with arthritis in the U.S. have one or more other serious health problems. Total joint replacement has been shown to restore mobility, relieve pain, and help osteoarthritis patients return to normal life.
Quality of Life
Quality of life is an important concept when considering the value medical technology brings to patients. Broadly speaking, quality of life can be thought of as an individual’s general sense of well-being. Health problems can interfere with the most basic aspects of daily living—for example, breathing comfortably, quality of sleep, eliminating waste, feeding oneself, intimacy, and others. When everyday functions such as these are negatively impacted, a person’s quality of life is significantly diminished. For a wide range of medical conditions that adversely impact quality of life, medical technology provides solutions that allow individuals to lead full, independent and productive lives, greatly increasing their quality of life.
Wound Care
Wounds are breaches in the structure of the skin that compromise skin function. They can be painful and lead to additional medical complications. Wounds become chronic when they have not completed the healing process in the expected timeframe, usually within 30 days. Medical technology has helped to evolve wound treatment dramatically over the past 15 years. From simple dressings to sophisticated, evidence-based options that treat and promote wound healing, patient benefits include lowered incidence of readmission, additional surgeries, and complications; reduced amputation rates; reduced healing times; and reduced incidence of surgical dehiscence and infection.
Healthcare-Associated Infections
Some 1.7 million patients acquire healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in U.S. hospitals each year, resulting in 99,000 deaths and $20 billion to $45 billion in additional health care costs. Diagnostic tests are a first-line defense against HAIs, capable of screening asymptomatic individuals to identify risk; detecting disease at the earliest stages before symptoms occur; and identifying threats to patient safety and public health. They also can be used to select safe and effective treatments, plan disease management strategies and estimate treatment response throughout the course of care. Tests for HAIs include viral cultures and molecular typing of microbial pathogens.
The Story of Medtech
Millions of lives are improved every day because of advancements in medical technology.